If you experience a salty taste in your mouth after a tooth extraction, it could be due to the placement of resin-based materials such as sealants, bonds, cement, or composites after a dental procedure. This bad salty taste should resolve on its own after a couple of rinses or after an hour. Secondly, if the taste does not go away by itself, it could indicate something else like an infection, low hydration levels, missing or low nutrients in your diet, Sjogren’s, medication side effects, hormonal changes, or acid reflux.
Our sense of taste and smell is vital for our daily function as human beings. So when there are slight changes in it, it could indicate something is wrong with our health.
Not only is this change slightly annoying, but it also is a crucial warning system in our body that tells us to be conscious of what’s going on with our overall health.
According to research, humans can identify 5 tastes. They are sweet, bitter, sour, salty, and umami. These tastes add to the joy of dining and is a source of great pleasure.
When one of these tastes lingers during situations other than eating and is constantly present despite brushing and flossing, it could indicate other problems. Like, after effect of a dental procedure, a disease symptom, or a medication side effect.
Likely causes of salty taste in your mouth
Salty taste in your mouth can be due to obvious reasons like a dental procedure or, it can occur due to underlying diseases and medications.
Sometimes dental procedures can overlap with a disease symptom. In that case, you may be suffering from something more serious and may not even be aware of it. Let us look into some reasons why we may be experiencing a salty taste in our mouths.
1. Infection

Infection is one of the most common causes of the salty taste. An abscess, infection of your gums (gingivitis) or, your jawbone can be the primary culprit. If left untreated, gingivitis can develop into periodontitis (gum disease).
When an abscess drains into your mouth, that is the time when you get the salty taste because of the pus and blood present in it.
There is often no or very little pain in the early stages of infection in your mouth. So, you may be suffering from it for weeks and months and can be unaware of the problem.
This is a dangerous situation because a lesser time taken for the infection to be noticeable can be crucial to avoid damage to other organs such as your heart and pancreases.
The bacteria in the abscess or infection areas can get into your bloodstream and can pose a threat to your health by making you susceptible to heart disease, diabetes, or stroke.
That is why you must get in touch with your dentist if you happen to experience a bad taste in your mouth or a salty taste in your mouth immediately.
2. Dental fillings
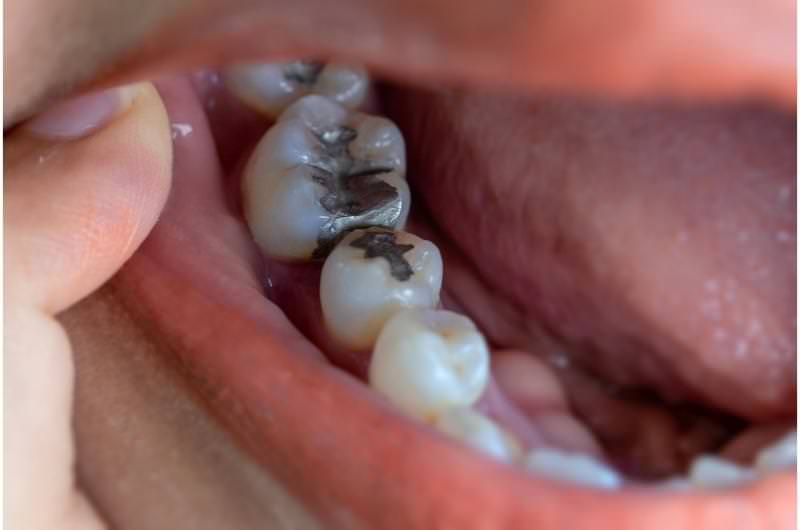
After your dentist has performed a procedure that involves dental fillings, it can cause a bad taste or salty taste in your mouth.
Even old, poorly maintained fillings can result in a salty taste or breath. It can taste salty or metallic over time if the filling is falling apart inside your mouth.
Silver mercury fillings can disintegrate where they are attached to the tooth. It can allow bacteria into the teeth’ surface, which can result in a peculiar salty taste.
With older fillings, we must be able to identify the problem early on and replace it. If this is not done early on, it can be potentially dangerous. As it can progress, decay faster and lessen the chances of the tooth being saved.
Visit your dentist if you experience recurring problems due to bad dental fillings.
3. Disease symptom
It is important to know the cause of the salty taste in the mouth to treat it. Many underlying diseases can also be the main reason for the salty taste after tooth extraction. They are as follows.
Xerostomia or dry mouth:
Xerostomia (reduced saliva production) can cause dryness in your mouth along with the following signs and symptoms:
- Bad breath
- Sore throat
- Stickiness in your mouth
- Thick saliva
- Hoarseness in your voice
- Rough tongue
Be sure to hydrate yourself by drinking a lot of water, reducing salty and spicy foods. You can also try an oral rinse for dry mouth to help stimulate the production of saliva.
Dehydration:
It is often caused due to excessive vomiting and diarrhea. Other signs and symptoms of dehydration are:
- Dizziness
- Fatigue
- Dark urine
- Confusion
- Extreme thirst
- Less urination
It can be life-threatening if not treated. Most people can get better by drinking water or receiving fluids intravenously.
Mucus, when swallowed unconsciously, can lead to a build-up in the back of your throat called postnasal drip. It also commonly occurs in sinus infections and during seasonal allergies.
When this mucus mixes with the saliva, it leads to a salty taste in your mouth.
When stomach acid flows up into the food pipe, it can also lead to a salty taste when it reaches your mouth. With salty taste, you may also experience:
- Pain in your abdomen
- Heartburn
- Cough
- Weight loss
- Bile in your vomit
If acid reflux is left untreated, it can lead to various diseases like Barrett’s esophagus, GERD( gastroesophageal reflux disease), or esophageal cancer.
Nutritional deficiency:
A salty or metallic taste in your mouth can indicate nutritional deficiencies. It can develop quickly or over the years. Other associated symptoms are:
- Pallor (pale skin)
- Fatigue
- Heartbeat irregularities
- Numbness in extremities
An immune system disorder, affecting all the fluid-producing glands in the body leading to a salty taste in the mouth. Other associated symptoms include:
- Dry eyes and mouth
- skin rashes
- Dry cough
- Vaginal dryness
- Fatigue
- Joint pain
Many manage this condition with oral over-the-counter treatments like oral rinses or prescription medications.
Other potential causes
A salty taste could also be the result of:
Hormonal changes
Hormonal changes accompanied during pregnancy can make your gums more sensitive and lead to bleeding, which causes a salty taste in the mouth.
Medication
Many medications can cause a salty aftertaste. Speak to your doctor if you think your medication is the cause of the taste-related changes.
Chemotherapy
Dry mouth or xerostomia is a common side effect of radiation, especially for those with head and neck cancers.
Chemotherapy also destroys the salivary glands and taste buds. So taste changes are expected in these treatment methods.
How to get rid of the salty taste after tooth extraction?
Aftercare of teeth extraction is very crucial for quick and proper healing. Be prepared to experience swelling and bleeding as a normal after-effect.
The following suggestions can help you with reducing the salty taste one can experience after an extraction.
- Place a gauze in your mouth to soak saliva and replace it when soaked.
- Drink plenty of water.
- Rinse with an antibacterial mouthwash every 3 or 4 hours.
- Reduce alcohol consumption or tobacco consumption.
- Eat soft, bland food to introduce a new taste.
- Take an antihistamine or decongestant to get rid of postnasal drip.
- Practice oral hygiene daily.
- Eat a well-balanced diet.
Takeaway
Teeth extraction is a routine procedure done very often. Recovery from an extraction is easy and smooth when you follow the aftercare instructions from your dentist.
In addition, it is also crucial to keep in mind other factors that may be an underlying cause of the salty taste in your mouth.
The reasons as mentioned earlier for salty taste should help you navigate your further plan of action if you are experiencing it often.